Wolf in sheep's clothing: Azure Active Directory reconnaissance as an insider
This post is part 3⁄5 of Azure AD and Microsoft 365 kill chain blog series.
Azure AD and Office 365 are cloud services and most information is hidden to the members (or guests) of the tenant. However, there are plenty of information publicly available to anyone.
In this blog, using AADInternals v0.4.5, I’ll show how to gather information of any Azure AD tenant as an insider.
Azure AD reconnaissance
Azure AD tenant information
An insider can retrieve the same information than a guest can.
So, first step is to get a access token for the target tenant and invoke the reconnaissance. The function will ask you to choose the target tenant:
# Prompt for credentials for tenant and save the token to cache
Get-AADIntAccessTokenForAzureCoreManagement -SaveToCache
# Invoke the reconnaissance and save results to a variable
$results = Invoke-AADIntReconAsInsiderTenant brand: Company Ltd
Tenant name: company.onmicrosoft.com
Tenant id: 6e3846ee-e8ca-4609-a3ab-f405cfbd02cd
Azure AD objects: 520/500000
Domains: 6 (4 verified)
Non-admin users restricted? True
Users can register apps? True
Directory access restricted? False
Directory sync enabled? true
CA policies: 8
MS Partner IDs: 8559542,8559543
MS Partner DAP enabled? False
MS Partner contracts: 5
MS Partners: 1
When compared to what a guest can see, here are some extra information. The status of directory synchronization is shown along with the number of global admins.
To list all admin roles and their “members”:
# List all admin roles that have members
$results.roleInformation | Where Members -ne $null | select Name,MembersName Members
---- -------
Company Administrator {@{DisplayName=MOD Administrator; UserPrincipalName=admin@company.onmicrosoft.com}, @{D...
User Account Administrator @{DisplayName=User Admin; UserPrincipalName=useradmin@company.com}
Directory Readers {@{DisplayName=Microsoft.Azure.SyncFabric; UserPrincipalName=}, @{DisplayName=MicrosoftAzur...
Directory Synchronization Accounts {@{DisplayName=On-Premises Directory Synchronization Service Account; UserPrincipalName=Syn...
With this information, we can focus to certain targets, such as Global Administrators. Also Directory Synchronization Accounts are interesting targets, as they can easily get Global Admin rights.
Note! Global admins can also be listed with:
Get-AADIntGlobalAdminsDirectory synchronization settings are also extremely valuable information.
To list synchronization information:
# List synchronization information
$results.companyInformation | Select *Sync*DirSyncAnchorAttribute : mS-DS-ConsistencyGuid
DirSyncApplicationType : 1651564e-7ce4-4d99-88be-0a65050d8dc3
DirSyncClientMachineName : SERVER1
DirSyncClientVersion : 1.5.30.0
DirSyncServiceAccount : Sync_SERVER1_abc123456@company.onmicrosoft.com
DirectorySynchronizationEnabled : true
DirectorySynchronizationStatus : Enabled
LastDirSyncTime : 2020-08-03T15:29:34Z
LastPasswordSyncTime : 2020-08-03T15:09:07Z
PasswordSynchronizationEnabled : true
The output shows the name of the synchronization server (SERVER1) and the service user name (Sync_SERVER1_abc123456@company.onmicrosoft.com).
With this information, we can target the synchronization server to extract credentials used in synchronization.
Note! Synchronization configuration can also be shown with:
Get-AADIntSyncConfigurationUser enumeration
As an insider, you have a read-only access to all users of Azure AD and to most of the attributes.
Lets start by running the user and groups enumeration. By default, the 1000 first users and groups are returned.
# Invoke the user enumeration
$results = Invoke-AADIntUserEnumerationAsInsider -GroupsUsers: 5
Groups: 2
Now you have a exported all users and groups (including Teams) from the Azure AD!
You have the following information about all users, including identity information for both Azure AD and on-prem (if synced). Similar information is also available for the groups.
# List the first user's information
$results.Users[0]displayName : User Demo
userPrincipalName : User@company.com
onPremisesImmutableId : UQ989+t6fEq9/0ogYtt1pA==
onPremisesLastSyncDateTime : 2020-07-14T08:18:47Z
onPremisesSamAccountName : UserD
onPremisesSecurityIdentifier : S-1-5-21-854168551-3279074086-2022502410-1104
refreshTokensValidFromDateTime : 2019-07-14T08:21:35Z
signInSessionsValidFromDateTime : 2019-07-14T08:21:35Z
proxyAddresses : {smtp:User@company.onmicrosoft.com, SMTP:User@company.com}
businessPhones : {+1234567890}
identities : {@{signInType=userPrincipalName; issuer=company.onmicrosoft.com; issuerAssignedId=User@company.com}}
Detecting
Azure AD sign-in log is now available for all Azure AD editions. So, this would be an obvious place to start with. However, the AADInternals functions are using the application id of Microsoft Office (d3590ed6-52b3-4102-aeff-aad2292ab01c). This means that getting a new access token seems to be a legit login event.
The API calls to Azure AD are not logged and therefore the users’ actions can not be detected.
Denial-of-Service attacks
Filling Azure AD with user objects
As explained in the blog post, if users are allowed to join devices to Azure AD, they can create so called Bulk PRT (BPRT) tokens.
Technically, BPRTs are user objects named as “Package_
Filling Azure AD with device objects
The number of devices users can join to Azure AD can also be limited. Typically, this limit is less than 20 devices per user. However, using a BPRT allows users to create any number of device objects until the tenant’s object limit is reached.
Detecting
There are various events that can be used to detect rogue behaviour (see blog for details):
- Review Audit Log for “Windows Confieguration Designer (WCD)” consent
- Review Audit Log for users created by “Microsoft.Azure.SyncFabric”
- Review Sign-ins log for sign-ins using non-WCD clients for “Device Registration Service (DSR)” resource
- Review Sign-ins log for sign-ins using “AADJ CSP” client id with out resource
- Review Sign-ins log for sign-ins using “AADJ CSP” client id for DSR resource
- Review Audit Log for events of type “Add registered owner to device” where targe user’s upn starts with “package_”
Preventing
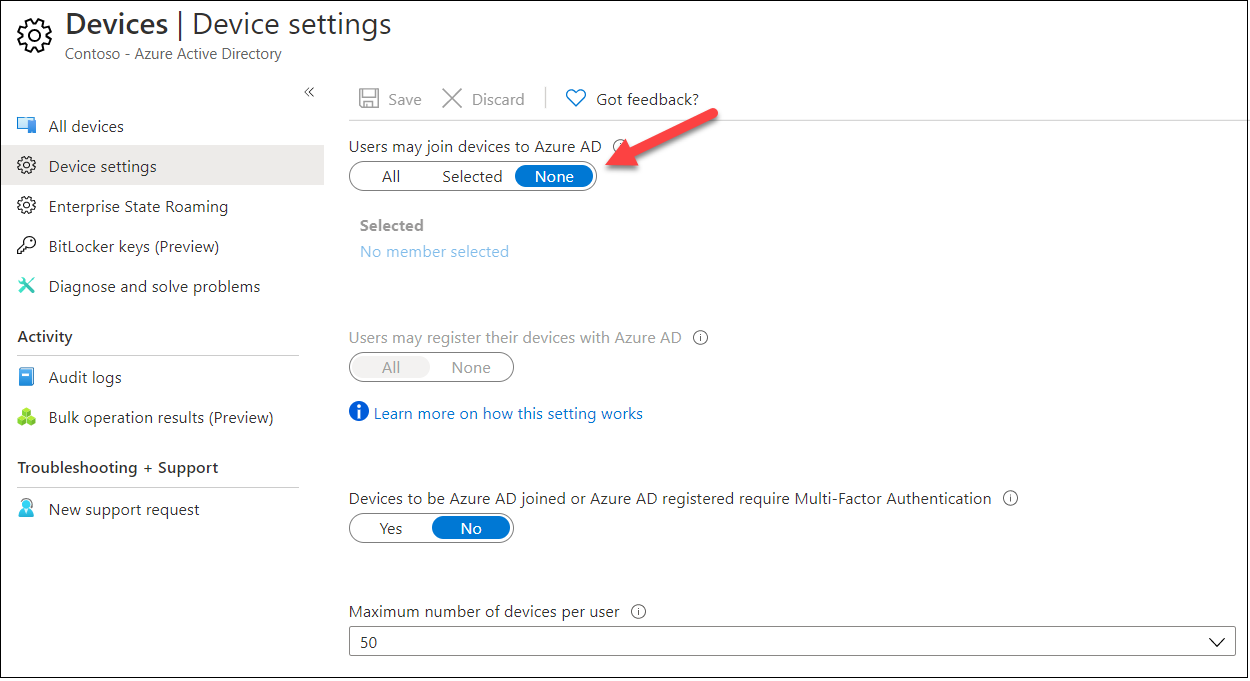
Only way to prevent users to create BPRTs is to prevent users to join devices to Azure AD:
Summary
As a regular user, you can read all the users and groups without any fear of getting caught!
Exporting the whole AzureAD took only a few minutes for organisation having 50 000 users and 15 000 groups.
Users are also able to fill the Azure AD with user or device objects. Luckily, this behaviour can be detected and the process is slow (20 users per minute and 90 devices per minute) so it can be mitigated quite easily. Only way to prevent this is to prevent users to join devices to Azure AD.
